Can You Use Ddr4 in a Ddr3 Slot
What is DDR4?
Double data charge per unit fourth generation (DDR4) is a retention standard designed as a improve, faster, more reliable replacement for DDR3.
How does DDR4 differ from DDR3 in appearance?
Physically, a DDR4 module, or dual in-line retentiveness module (DIMM), looks very like to a DDR3 DIMM. However, DDR4 has 288 pins compared with DDR3's 240 pins; DDR4 And so-DIMMS take 260 pins instead of 204 in DDR3. The DDR4 key notch is in a different place, and the edge connector looks like a slightly curved "Five" to facilitate insertion. This blueprint likewise lowers insertion force, as not all pins are engaged at the aforementioned fourth dimension during module insertion.
DDR Cardinal Notch Positions
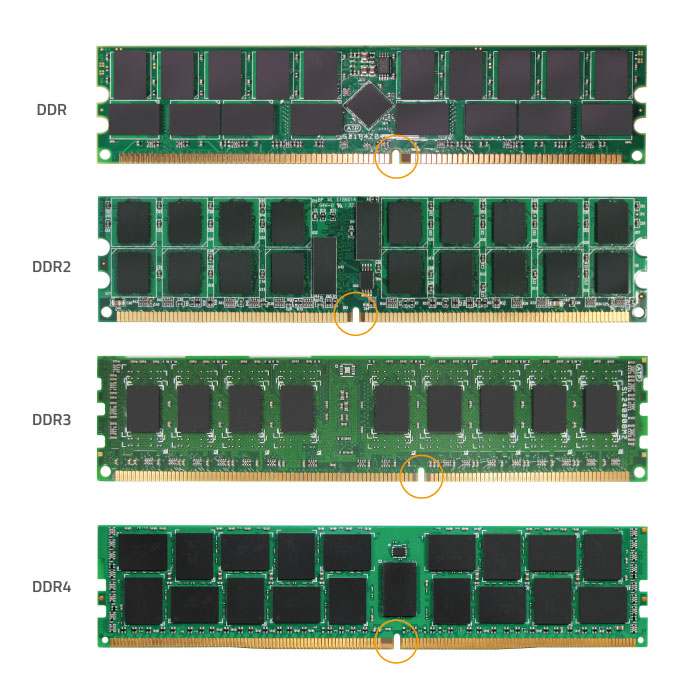
Figure 1. The pin count and fundamental notch location for each DDR generation are dissimilar.
How does DDR4 differ from other DDR generations?
The following tabular array compares the different DDR generations.
DDR Development
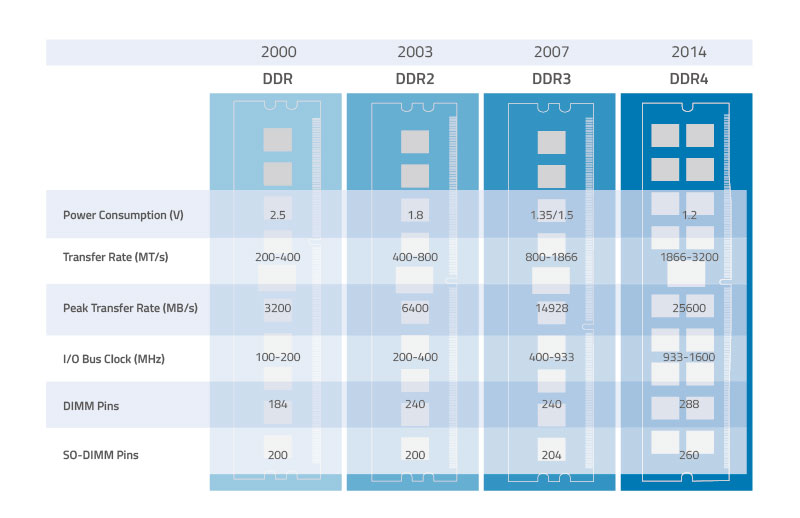
Table 1. Comparison of different DDR generations
What are the advantages of DDR4 over DDR3?
Lower ability
DDR4 modules are more free energy-efficient, operating only at 1.2V compared with DDR3'south 1.5V or i.35V. The reduced power consumption gives substantial power savings and allows operation at college speeds without higher power and cooling requirements.
College module density
DIMM densities start at 2 GB, reaching upwards to 128 GB – a big leap from DDR3's 512 MB to 32 GB capacities.
Faster data transfer speed
ATP'south latest DDR4 modules for embedded and industrial applications deliver high-speed information transfers up to 3200 MT/s. DDR4-3200, the latest industrial DDR4 offering from ATP, transfers data near 70% faster than DDR3-1866, one of the fastest DDR3 versions bachelor, for a big boost in theoretical peak performance.
| Item | DDR3-1866 | DDR4-3200 |
|---|---|---|
| I/O bus clock | 933 MHz | 1600 MHz |
| Data rate | 1866 MT/s | 3200 MT/due south |
| Peak transfer rate | 14928 MB/due south | 25600 MB/s |
Table 2. DDR3-1866 vs. DDR4-3200
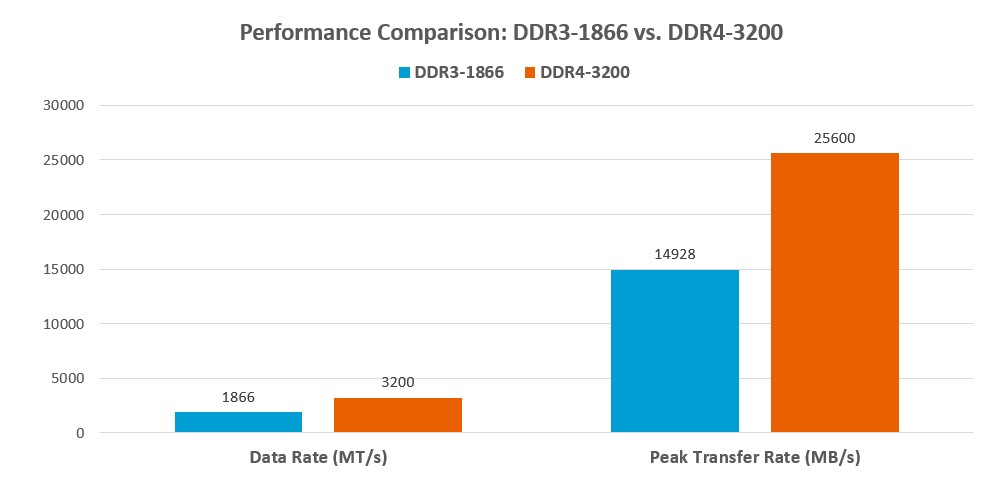
Figure two. Performance comparing: DDR3-1866 vs. DDR4-3200.
Do the latest Intel® Xeon® Scalable processors support DDR4 modules from ATP?
Yes. Each of the latest Intel® Xeon® Scalable processors with Intel® C620 Series Chipsets (formerly code-named Skylake-SP and Lewisburg) provides native support for six retentivity channels that can operate at the same speed even at full load. Each memory channel supports two DIMMs, which means each processor can support up to 12 DIMMs. Having ii additional retention channels compared with the previous quad-channel platform delivers a pregnant increase in speed and performance. Aside from Intel® Xeon® Scalable processors, DDR4-2666 is also built for 8th Gen Intel® Core™ Processors.
Which applications and industries will benefit well-nigh from DDR4-3200/2933/2666/2400?
The increased interface speed amplifies theoretical peak operation for the most disquisitional computing applications in industries such equally telecommunication infrastructures, networking storage systems, network-attached storage (NAS) servers, micro/cloud servers, and embedded systems like industrial PCs.
What DDR4 DIMM grade factors are available from ATP Electronics?
| Form Factor | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category | LRDIMM | RDIMM | UDIMM | UDIMM ECC | SO-RDIMM | And so-DIMM | And then-DIMM ECC | Mini-RDIMM | Mini-UDIMM | Mini-UDIMM ECC |
| Information Charge per unit Speed (MT/south) | 3200 2933 2666 2400 2133 | 2400 2133 | 3200 2933 2666 2400 2133 | 2400 2133 | ||||||
| PCB Height | Low profile | VLP: 0.74" meridian | ||||||||
| VLP option: 0.74" height | ULP option: beneath 0.74" pinnacle | VLP option: 0.74" height | VLP pick: 0.74" height | |||||||
| Density | 32 GB 64 GB 128 GB | four GB eight GB xvi GB 32 GB 64 GB 128 GB | two GB 8 GB 16 GB 32 GB | iv GB 8 GB xvi GB 32 GB | 2 GB 8 GB 16 GB 32 GB | 4 GB 8 GB 16 GB 32 GB | ||||
| Voltage | 1.2V | |||||||||
| Working Temperature | Wide Temp: -twoscore-95°C Commercial Class: 0-85°C | |||||||||
| Golden Finger | 30µ | |||||||||
Table three. ATP DDR4 product family
How will I know if my arrangement supports DDR4? Can I install a DDR4 DIMM on a DDR3 slot?
Every DDR generation is unlike from the others. DDR4 is not backward-compatible with DDR3 so a DDR4 DIMM will not fit on a DDR3 DIMM slot. Not only is the key notch of each DDR generation unlike (delight refer to Figure 1 above), simply the DDR4 pivot size and arrangement is dissimilar from DDR3. Notice that towards the middle of the DDR4 module, some pins are longer, giving information technology a slightly curved "V" shape. Refer to your motherboard documentation to make certain that it has the correct DDR4 slot.
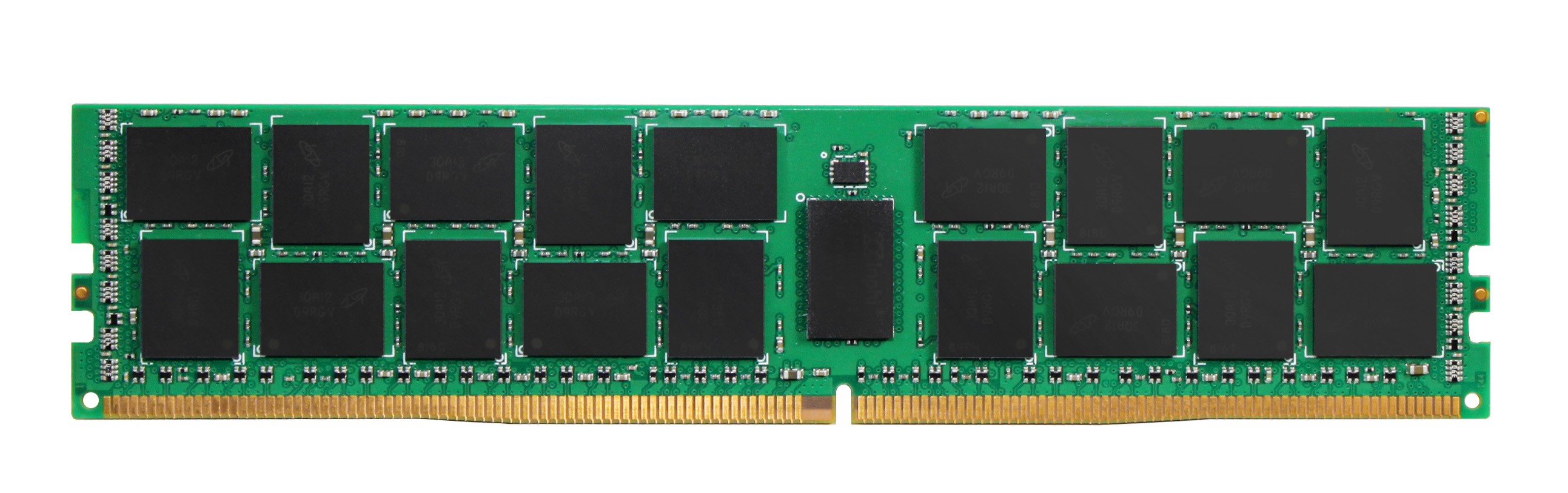
Figure 3. A standard DDR4 ECC DIMM module from ATP. Pins in the eye are longer, giving the module a slightly curved "V" shape.
How can I cull which DIMM blazon to employ on my system?
Dissimilar DIMM types serve several purposes. DIMMs may or may not have error correcting code (ECC/non-ECC). They could be unbuffered or fully buffered (UDIMM/FB-DIMM), registered (RDIMM), or load-reduced (LR-DIMM). Different systems platforms can accommodate different memory types, and then make sure to check which DIMMs are supported on your motherboard. For a quick look at common retentiveness types, read "Understanding RAM and DRAM Estimator Retention Types" on the ATP Web log.
Is information technology possible to combine DIMMs with different data rates on the same system?
To get the best memory functioning, it is recommended that you install identical DIMMs on the same organisation. When mixing DIMMs of unlike operating speeds, the motherboard will underclock the faster one so it volition merely run at the speed of the slowest DIMM, unless you overclock the slow DIMMs. DIMM population guidelines may vary depending on the platform you are using. Refer to the server motherboard documentation for detailed instructions.
Source: https://www.atpinc.com/blog/ddr4-vs-ddr3-differences-advantages
0 Response to "Can You Use Ddr4 in a Ddr3 Slot"
ارسال یک نظر